Manufacturing is a dynamic process, one in a constant state of flux. Many suppliers adopted lean principles, which have been popular since the 1980s. Industry 4.0, which emerged in the last decade, is a concept that focuses on using new technology to improve manufacturing processes. The two have similar goals but different areas of emphasis. Their implementations work best when manufacturing companies use them together, and a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) helps to connect them.
What is Lean and Industry 4.0?
Lean manufacturing, also known as lean production, Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing, and Just-In-time Production, is a manufacturing methodology. The goal is to reduce the frequency and time that materials and personnel spend sitting idle somewhere in the supply chain or among manufacturing processes. Such delays drive up expenses, create inefficiencies, and reduce customer satisfaction. Lean manufacturing focuses on continuous improvement and companies continually tweaking their workflow. The ultimate goal is to have materials and manpower arrive right when they are needed on the plant floor.
Lean manufacturing is most closely associated with automobile manufacturing operations, specifically the Toyota Production System. Nowadays, Lean has been generally accepted as a manufacturing best practice. Just about all large volume production facilities in every industry have adopted at least a few of its tenets. Smaller volume production facilities have also implemented lean processes to create smart factories.
Industry 4.0 is based on the notion that recent technology advances, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud, mobile, and Augmented Reality/Virtual Reality, offer suppliers the opportunity to dramatically improve manufacturing processes. With digitization, these companies streamline their supply chains and enhance manufacturing production.
Lean and Industry 4.0 Similarities and Differences
Both lean and Industry 4.0 are manufacturing philosophies or frameworks with the goal of strengthening manufacturing operations. Potential benefits include items like increased efficiency, higher productivity, reductions in machine downtime, faster cycle times, improved supply and demand matching, more visibility and traceability in supply chains and production floor, enhanced customer satisfaction, and revenue growth.
But they have different focuses. Lean manufacturing is primarily about business processes and is technologically agnostic. It works in a legacy low technology environment just as well as in a modern digital environment. Industry 4.0 leverages advanced technology to create integrated, highly adaptive, automated manufacturing production runs.
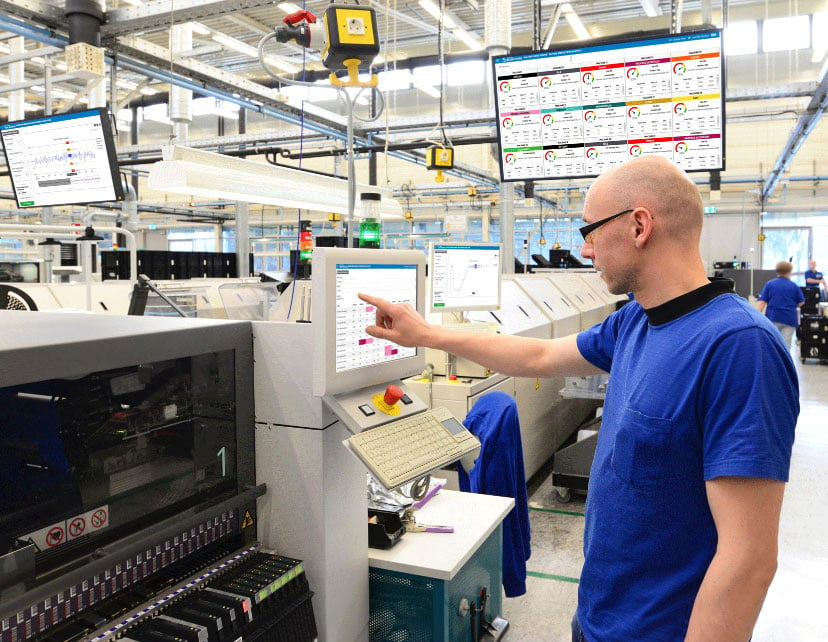
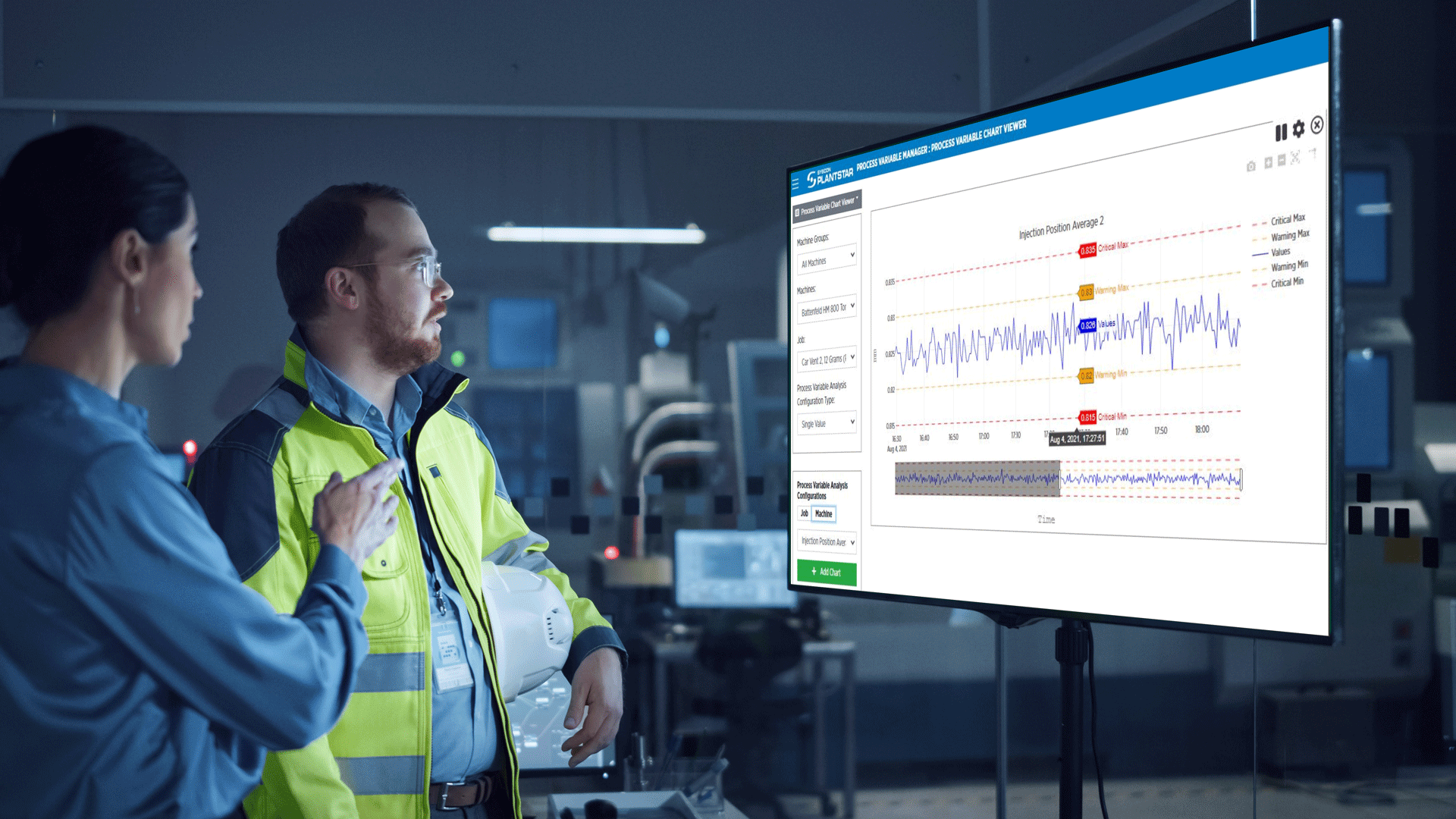
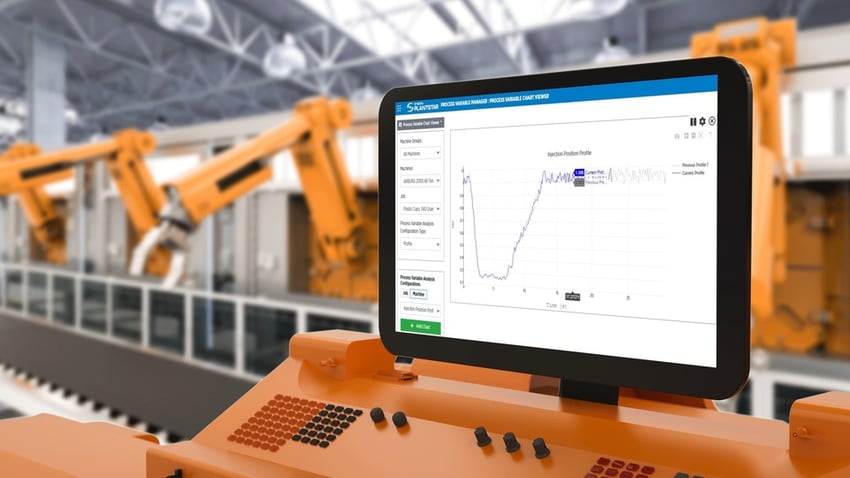
These approaches try to overcome traditional manufacturing shortcomings, such as limited visibility into daily operations. An MES empowers both Lean and Industry 4.0 by collecting data in a central repository and providing manufacturing production and supply chain applications with access to it. An MES solution, such as PlantStar, supports Production Monitoring, which tracks how quickly parts are produced, and Process Monitoring, which measures different variables, such as temperature, pressure, and hold time, that impact equipment performance.
Many suppliers have embraced lean but need to upgrade their manufacturing technology infrastructure in order to board the Industry 4.0 train. Digital technology reduces the need for items, like whiteboards, physical Kanban cards, and Andon cords, which have been part of legacy Lean solutions.
Coupling both works best for suppliers. Manufacturing companies that have embedded Lean into their operations are positioned to gracefully embrace the digital era. In fact, Boston Consulting Group found that a combined Lean and Industry 4.0 approach reduces costs by 40% as opposed to only 15% if digitization and Lean are applied separately. Here are a few ways that the two principles mesh.
Benefits of Coupling Lean and Industry 4.0
Digitization of Supply Chains Enhances JIT. JIT demands accurate and timely inventory information. By digitizing supply chains and factory floors, manufacturers gain transparency into where materials and goods are. Therefore, they are better able to track inventory accurately and have more data available to forecast better. If problems arise, they can make adjustments and mitigate any shortfalls.
Automate More Functions. Manufacturing’s reliance on manual processes was one reason for its inefficiencies. Automation enables suppliers to replace such tasks with computer-generated responses. Examples include firing off an alert when a machine looks like it may soon be knocked out of service.
Automation is a key in predictive maintenance, which reduces downtime by reporting deviations faster, conducting root-cause analyses of failures, and automatically initiating corrective actions. Thus, Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) improves as machine shortcomings are reduced.
Improve Training with Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality. Handling large and small equipment can be challenging. Training has been ineffective at times because it often lacked hands-on application. Virtual Reality and Augmented reality provide employees typically with head-mounted devices that mimic real-world situations. Therefore, they train operators in autonomous maintenance realistically and they gain the knowledge needed to perform such tasks.
Manufacturing is nearing another transition point. Industry 4.0 promises to improve factory operations by enhancing technology and data collection. Pairing it with Lean manufacturing and an MES solution enables suppliers to work with real-time information, automate manual functions, reduce costs, and boost revenue. In sum, the new improvements boost operations and enable manufacturers to make their organizations even leaner.